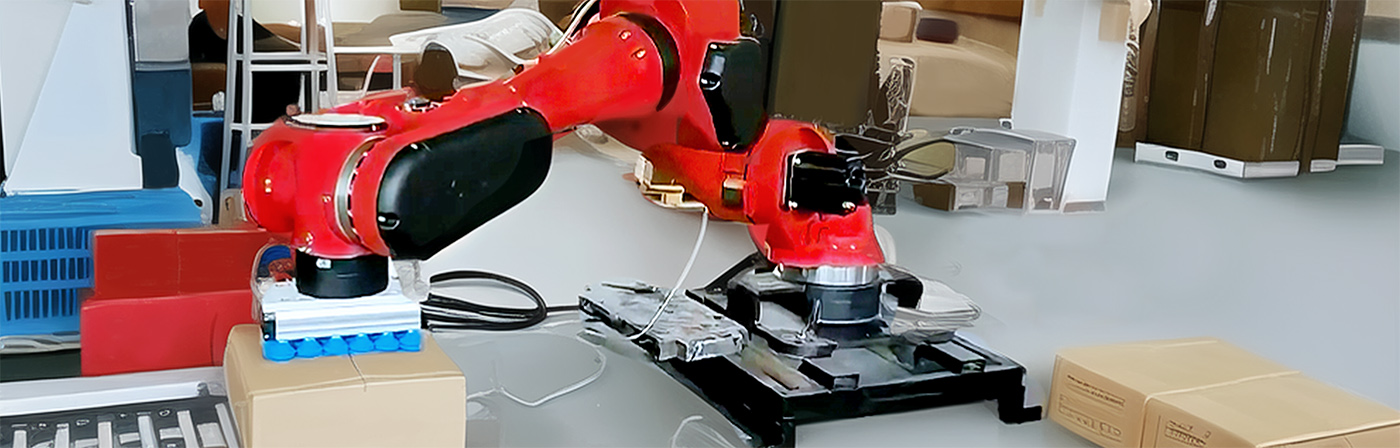
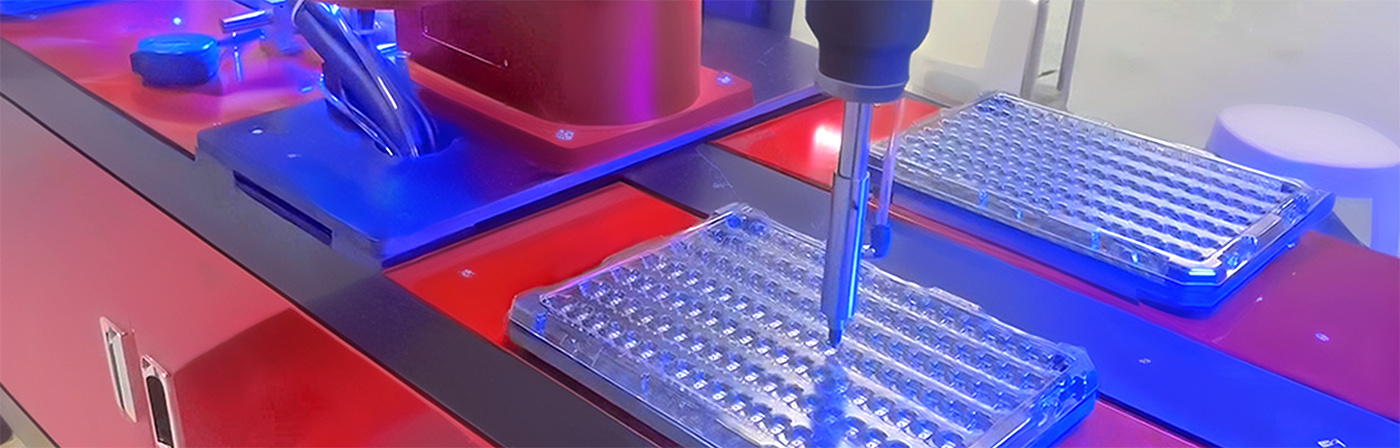
BRTIRPL1003A type robot is a four-axis robot that developed by BORUNTE for assembly, sorting and other application scenarios of light, small and scattered materials. The maximum arm length is 1000mm and the maximum load is 3kg. The protection grade reaches IP40. The repeat positioning accuracy is ±0.1mm.

Accurate Positioning

Fast

Long Service Life

Low Failure Rate

Reduce Labor

Telecommunication
|
Item |
Range |
Range |
Max speed |
||
|
Master Arm |
Upper |
Mounting surface to stroke distance 872.5mm |
46.7° |
stroke:25/305/25(mm) |
|
|
Hem |
86.6° |
||||
|
End |
J4 |
±360° |
150 time/min |
||
|
|
|||||
|
Arm Length (mm) |
Loading Ability (kg) |
Repeated Positioning Accuracy (mm) |
Power Source (kVA) |
Weight (kg) |
|
|
1000 |
3 |
±0.1 |
3.18 |
104 |
|

1.What is a four-axis parallel robot?
A four-axis parallel robot is a type of robotic mechanism that consists of four independently controlled limbs or arms connected in a parallel arrangement. It is designed to provide high precision and speed for specific applications.
2.What are the advantages of using a four-axis parallel robot?
Four-axis parallel robots offer advantages such as high stiffness, accuracy, and repeatability due to their parallel kinematics. They are suitable for tasks requiring high-speed motion and precision, such as pick-and-place operations, assembly, and material handling.

3.What are the main applications of four-axis parallel robots?
Four-axis parallel robots are commonly used in industries such as electronics manufacturing, automotive assembly, pharmaceuticals, and food processing. They excel in tasks like sorting, packaging, gluing, and testing.
4.How does the kinematics of a four-axis parallel robot work?
The kinematics of a four-axis parallel robot involve the movement of its limbs or arms in a parallel configuration. The end-effector's position and orientation are determined by the combined motion of these limbs, which is achieved through careful design and control algorithms.
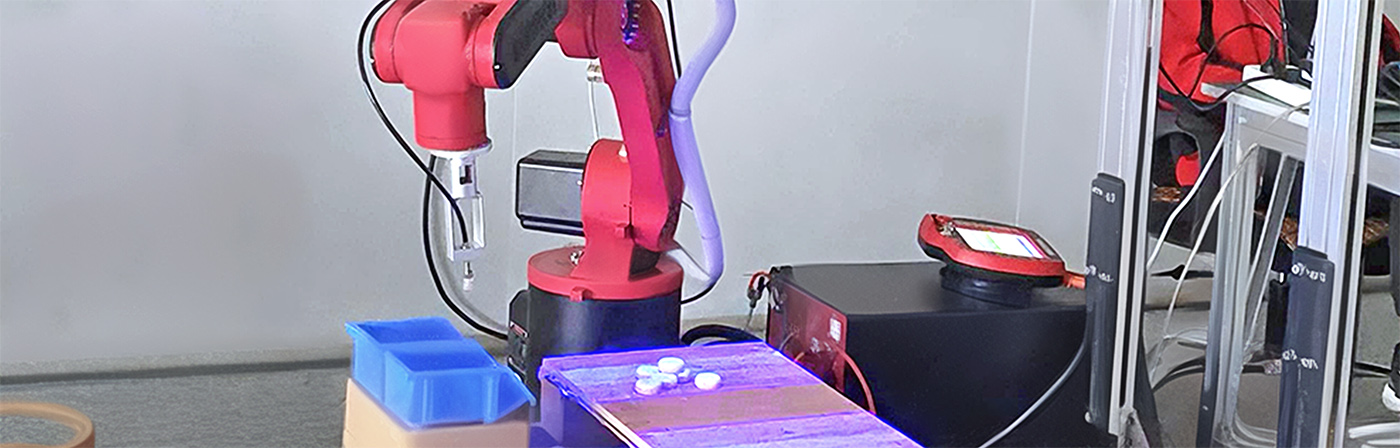
1.Lab Automation:
Four-axis parallel robots are used in laboratory settings for tasks such as handling test tubes, vials, or samples. Their precision and speed are crucial for automating repetitive tasks in research and analysis.
2.Sorting and Inspection:
These robots can be employed in sorting applications, where they can pick and sort items based on certain criteria, such as size, shape, or color. They can also perform inspections, identifying defects or inconsistencies in products.

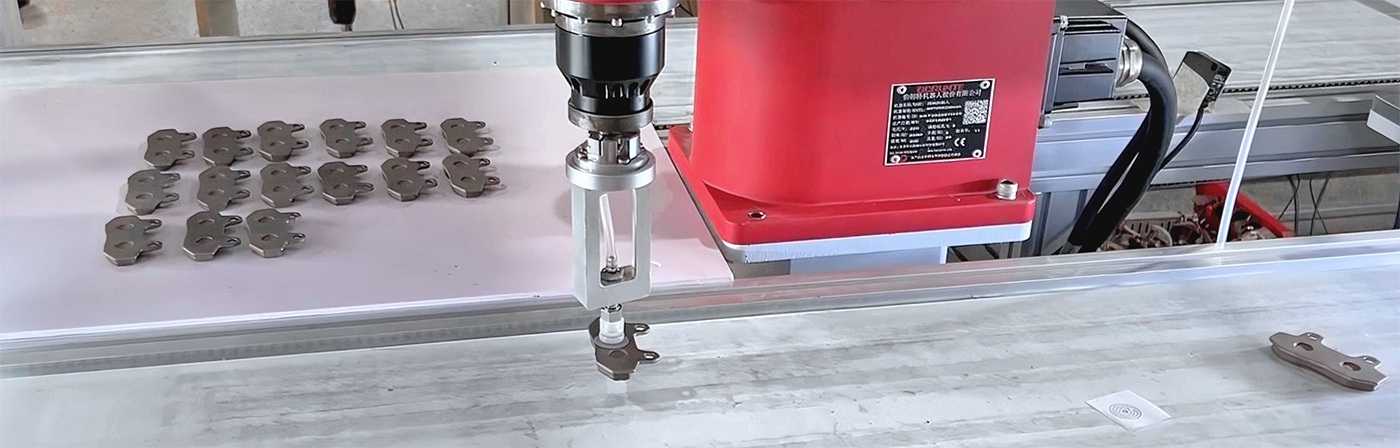
3.High-Speed Assembly:
These robots are ideal for high-speed assembly processes, such as placing components onto circuit boards or assembling small devices. Their rapid and accurate movement ensures efficient assembly line operations.
4.Packaging:
In industries like food and consumer goods, four-axis parallel robots can efficiently package products into boxes or cartons. Their high-speed and accuracy ensure products are packed consistently and efficiently.
-
Transport
-

Detection
-
Vision
-
Sorting
Products categories
BORUNTE and BORUNTE integrators
In the BORUNTE ecosystem, BORUNTE is responsible for the R&D, production, and sales of robots and manipulators. BORUNTE integrators utilize their industry or field advantages to provide terminal application design, integration, and after-sales service for the BORUNTE products they sell. BORUNTE and BORUNTE integrators fulfill their respective responsibilities and are independent of each other, working together to promote the bright future of BORUNTE.
-
-
-

Top